Refractory Metal Laser Powder Bed Fusion Components for Energy Efficient High Temperature Furnaces
At Plansee SE, the development of the next generation of energy-efficient refractory metal hot zones for high-temperature vacuum furnaces is supported by numerical simulations.
High-temperature vacuum furnaces generally operate with power levels of several hundred kilowatts. They are typically equipped with a fast-cooling system to achieve the cooling rates necessary for heat treatment processes. However, the state-of-the-art design of the inlet gas nozzles and gas outlet leads to significant energy losses.
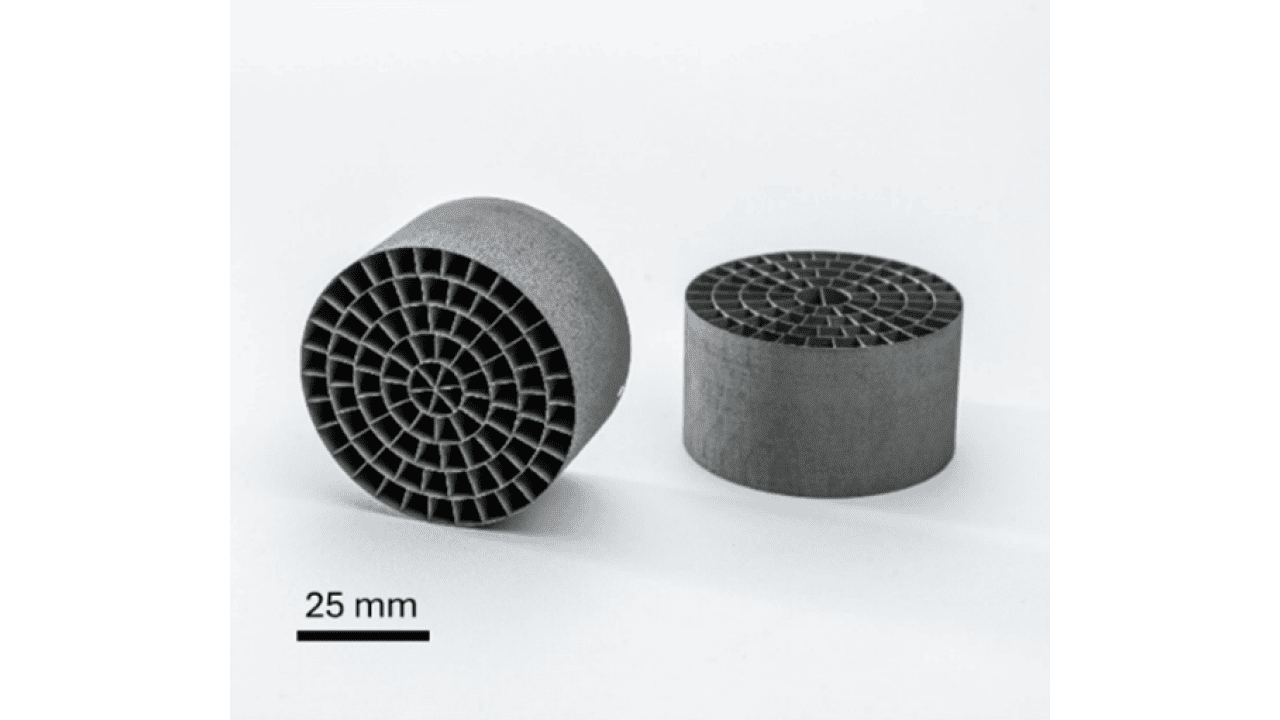
At Plansee SE, the development of the next generation of energy-efficient refractory metal hot zones for high-temperature vacuum furnaces is supported by numerical simulations. Based on multi-physical models thin-walled gas permeable structures shielding thermal radiation were developed. Prior to manufacturing, thermal and fluid dynamic models were employed to assess the performance of those components. The structures were fabricated by laser powder bed fusion of molybdenum and tested in a furnace to evaluate temperature uniformity, cooling efficiency and power consumption. The results demonstrate significant energy savings and improved temperature uniformity without compromising cooling efficiency.
Presentation language: GER
Speakers (1)