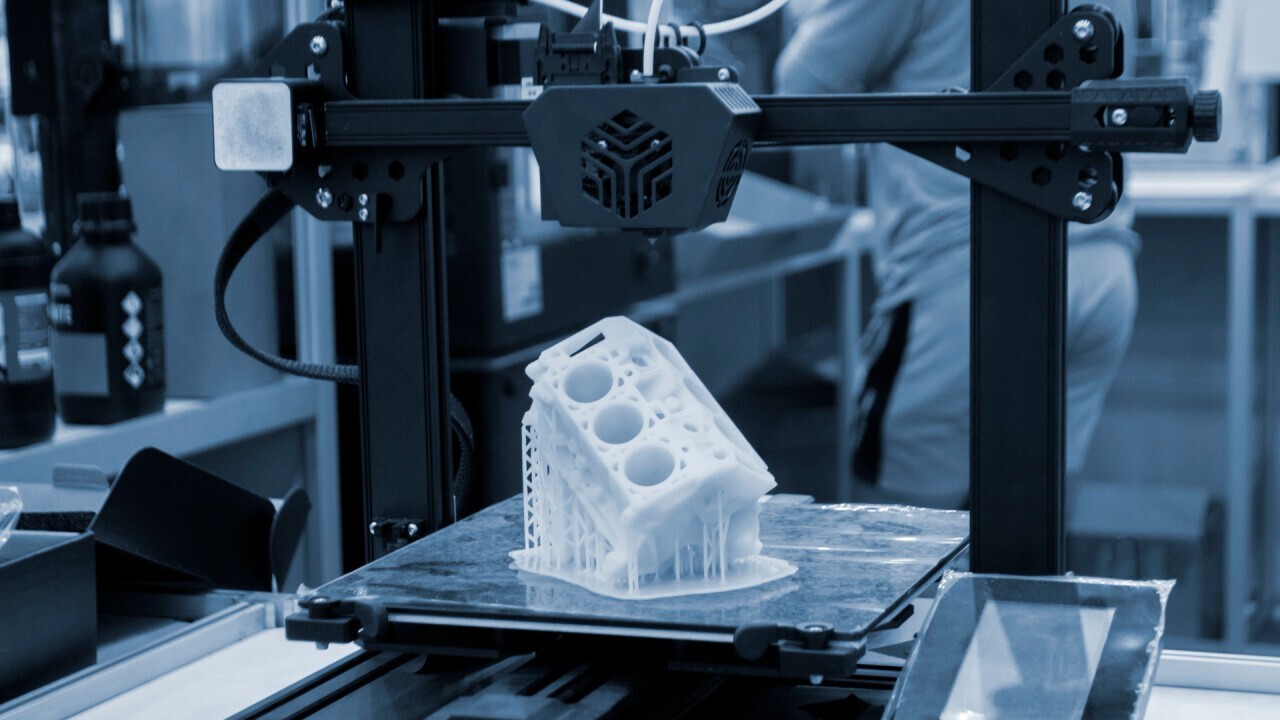
3D printing in the automotive industry
3D printing is changing the automotive industry: with faster prototype development, lightweight components and individual designs, manufacturing processes are becoming more efficient and flexible. The technology enables more sustainable vehicle production and opens up new possibilities for innovativ
The rapid advances in the field of 3D printing have fundamentally changed the way products are manufactured in various industries. In the automotive industry, this innovative manufacturing technology has become a key player, challenging traditional production processes and opening up new possibilities. From the first experiments to groundbreaking applications, 3D printing has found its place in automotive production. This development not only enables the efficient production of complex components and prototypes, but also paves the way for creative design and individual customization.
In this respect, the links between 3D printing and the automotive industry are examined in more detail. The technology not only enables technical challenges to be overcome, but also offers scope for innovative solutions and efficiency improvements. These advances not only have an impact on current production, but also provide a glimpse into the promising future of this dynamic interplay between 3D printing and the automotive industry. Experience 3D printing in the automotive industry up close at rapid.tech 3D and exchange ideas with the experts about the latest innovations.
The diverse application areas of 3D printing in the automotive industry
One of the most striking application areas is prototype development. 3D printing technologies enable manufacturers to quickly and cost-effectively create prototypes of vehicle parts. This significantly speeds up the development process and allows engineers to immediately review and adapt design ideas.
 Another crucial application area is the production of lightweight structures and components. By using 3D printing materials in the automotive industry, such as composites, car manufacturers can produce parts with optimized strength and weight reduction. This not only helps improve vehicle performance, but also supports the industry's efforts to create more sustainable and resource-efficient vehicles.
Another crucial application area is the production of lightweight structures and components. By using 3D printing materials in the automotive industry, such as composites, car manufacturers can produce parts with optimized strength and weight reduction. This not only helps improve vehicle performance, but also supports the industry's efforts to create more sustainable and resource-efficient vehicles.
Vehicle personalization is an emerging area in which 3D printing plays a crucial role in the automotive industry. Individual components, adapted to the customer's wishes, can be produced easily and inexpensively. This ranges from personalized dashboards to bespoke body panels, making vehicles unique expressions of their owners' personalities.
In addition to manufacturing components, 3D printing also enables the production of complex structures that would be difficult or impossible to produce using conventional manufacturing methods. The additive manufacturing of engine systems, such as cooling channels, plays a particularly crucial role here.
Material diversity in 3D printing for the automotive industry: plastics, metals and innovative composite materials in focus
Choosing the right materials plays a crucial role in 3D printing for the automotive industry and significantly influences the quality, strength and functionality of the printed parts. A variety of materials are used to meet the specific requirements of automotive production.
Plastics in the automotive industry
In the world of automotive 3D printing, plastics play a crucial role as they cover a wide range of applications and are suitable for both prototypes and final products. Different plastics are used depending on the specific requirements of the printed parts.
For prototyping and non-structural parts, ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), PLA (polylactic acid) and nylon are commonly used plastics. These materials are characterized by their ease of use, low cost and reasonable strength. 3D printing with these plastics enables rapid translation of design ideas into tangible prototypes, thus accelerating the innovation process in automotive development.
For structural components that need to withstand higher loads, more advanced plastics are used. Polyamide (PA), polycarbonate (PC) and polyetherimide (PEI) offer improved strength, durability and temperature resistance. These plastics are well suited for applications such as engine mounts, transmission housings and other parts that require structural integrity.

A particularly significant advance is the use of bio-based and recyclable plastics for 3D printing in the automotive industry. These materials contribute to sustainability in automotive production and enable more environmentally friendly solutions for components that are not only functional but also ecologically compatible.
The versatility and innovative power of plastics in 3D printing in the automotive industry help to improve efficiency, flexibility and sustainability in the automotive industry, while opening the door to new design possibilities and advanced manufacturing technologies.
Metal in the automotive industry
Metallic 3D printing has gained significant importance in the automotive industry as it enables the production of parts with high strength and precision. Various metals are used in the 3D printing process to produce components that meet the high demands of automotive production.
Aluminium is one of the commonly used metals in 3D printing. It is characterized by low density, good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Aluminium components produced using 3D printing find application in various parts of the vehicle, including housings, brackets and cooling components.
 Titanium is another important metal in 3D printing for the automotive industry. Titanium alloys offer high strength while remaining lightweight and are particularly suitable for applications where strength and weight reduction are critical. In the automotive sector, titanium is often used for components such as springs, brake parts and exhaust components.
Titanium is another important metal in 3D printing for the automotive industry. Titanium alloys offer high strength while remaining lightweight and are particularly suitable for applications where strength and weight reduction are critical. In the automotive sector, titanium is often used for components such as springs, brake parts and exhaust components.
Stainless steel is a versatile metal that is used for a wide range of applications in 3D printing. Various stainless steel alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance, strength and durability. Printed stainless steel parts can be found in vehicle components such as exhaust systems, fasteners, and even interiors. Metal 3D printing also enables the production of complex structures and geometric shapes that would be difficult to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods. This freedom in the design process helps improve the efficiency and performance of vehicle parts.
Innovative Composite Materials in the automotive industry
Innovative composite materials are playing an increasingly important role in 3D printing for the automotive industry, as they enable the production of lightweight, yet strong and resilient components. These materials combine different substances, such as plastics and fiber composites, to achieve optimal properties for specific applications.
An outstanding example of innovative composite materials in 3D printing in the automotive industry is carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP). CFRP combines the lightness of plastics with the high strength and rigidity of carbon fibers. This enables the production of components with exceptional strength while reducing weight. CFRP is used in the automotive industry in structural components such as body panels, bumpers and hoods.
 Another promising composite material is glass fiber reinforced plastic (GRP). GRP combines plastic with glass fibers, resulting in a material that is lightweight, inexpensive, yet robust. In 3D printing, GRP is often used for parts where weight reduction and cost efficiency are crucial, for example in the production of housings, panels and interior trim.
Another promising composite material is glass fiber reinforced plastic (GRP). GRP combines plastic with glass fibers, resulting in a material that is lightweight, inexpensive, yet robust. In 3D printing, GRP is often used for parts where weight reduction and cost efficiency are crucial, for example in the production of housings, panels and interior trim.
These composites enable engineers to produce components with tailored material properties that meet the specific requirements of different vehicle components. The 3D printing process also allows the implementation of complex shapes and structures, which, in combination with innovative composite materials, leads to further optimization of lightweight construction concepts in the automotive industry.
Advantages of 3D printing in the automotive industry
The use of 3D printing in the automotive industry offers a variety of benefits that optimize the entire production process and vehicle performance. Here are some of the outstanding benefits:
- Faster prototyping: 3D printing enables rapid production of prototypes, which significantly shortens the development cycle. Engineers can quickly translate design ideas into physical models to review and adjust if necessary.
- Weight reduction: By manufacturing lightweight structures and components, vehicles can be designed more efficiently. The use of materials such as composites and lightweight metals helps to reduce overall weight and thus optimize fuel consumption.
- More complex designs: 3D printing in the automotive industry allows the production of complex shapes and structures that would be difficult to achieve using conventional manufacturing methods. This enables engineers to realize innovative and optimized designs, which increases the efficiency and performance of vehicles.
- Cost efficiency: In prototype development and in the production of small series, 3D printing can achieve significant cost savings. The ability to produce parts locally and on demand reduces storage costs and enables more flexible production planning.
- Individual adaptations: 3D printing allows the cost-effective production of customized parts and components. This not only enables personalized vehicle design, but also the production of spare parts as needed.
- Sustainability: By using lighter materials and reducing production waste, 3D printing contributes to sustainability in the automotive industry. The possibility of local production can also minimize transport costs.

Challenges of 3D Printing in the automotive industry
Although 3D printing in the automotive industry has immense potential, there are also several challenges that need to be overcome:
- Material limitations: Some of the common 3D printing materials may not have the same mechanical properties as traditional materials, which can limit their application in certain critical parts. Finding innovative materials with optimal performance remains a challenge.
- High volume production: 3D printing is still less efficient in terms of high volume production compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Transferring 3D printing in the automotive industry to mass production at an economical cost remains a challenge.
- Print speed and scalability: Current printing speed for high-resolution and complex parts is often limited. The challenge lies in increasing printing speed without compromising on quality. In addition, scalability must be improved for the production of parts of different sizes and levels of complexity.
- Quality control: Ensuring consistent and high print quality is crucial, especially when it comes to safety-relevant components in automotive manufacturing. Implementing effective quality control procedures is an ongoing challenge.
- Cost and economics: The acquisition and operating costs of 3D printers and the materials used can be higher compared to traditional manufacturing methods. The automotive industry must find ways to improve the economics of 3D printing more broadly.
- Regulatory requirements: Integrating 3D printing into automotive production requires meeting strict regulatory standards and certifications. Achieving and maintaining these standards presents an additional challenge.

3D printing in the automotive industry: Future prospects for efficiency, innovation and individualization
The future of 3D printing in the automotive industry promises to be a fascinating development. A key development is the increased integration of 3D printing into the series production of vehicle parts, enabling more efficient manufacturing. Advances in 3D printing materials, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and increasing on-demand production will transform the industry. In the area of design, 3D printing will become even more integrated, giving designers the freedom to design complex and optimized structures. At the same time, 3D printing will further advance the customization and personalization of vehicles, from the body to individual interiors. Overall, the future of 3D printing in the automotive industry will be characterized by progressive innovation, increased efficiency, and individual design. The technology will continue to play a crucial role in how vehicles are developed, produced, and experienced.