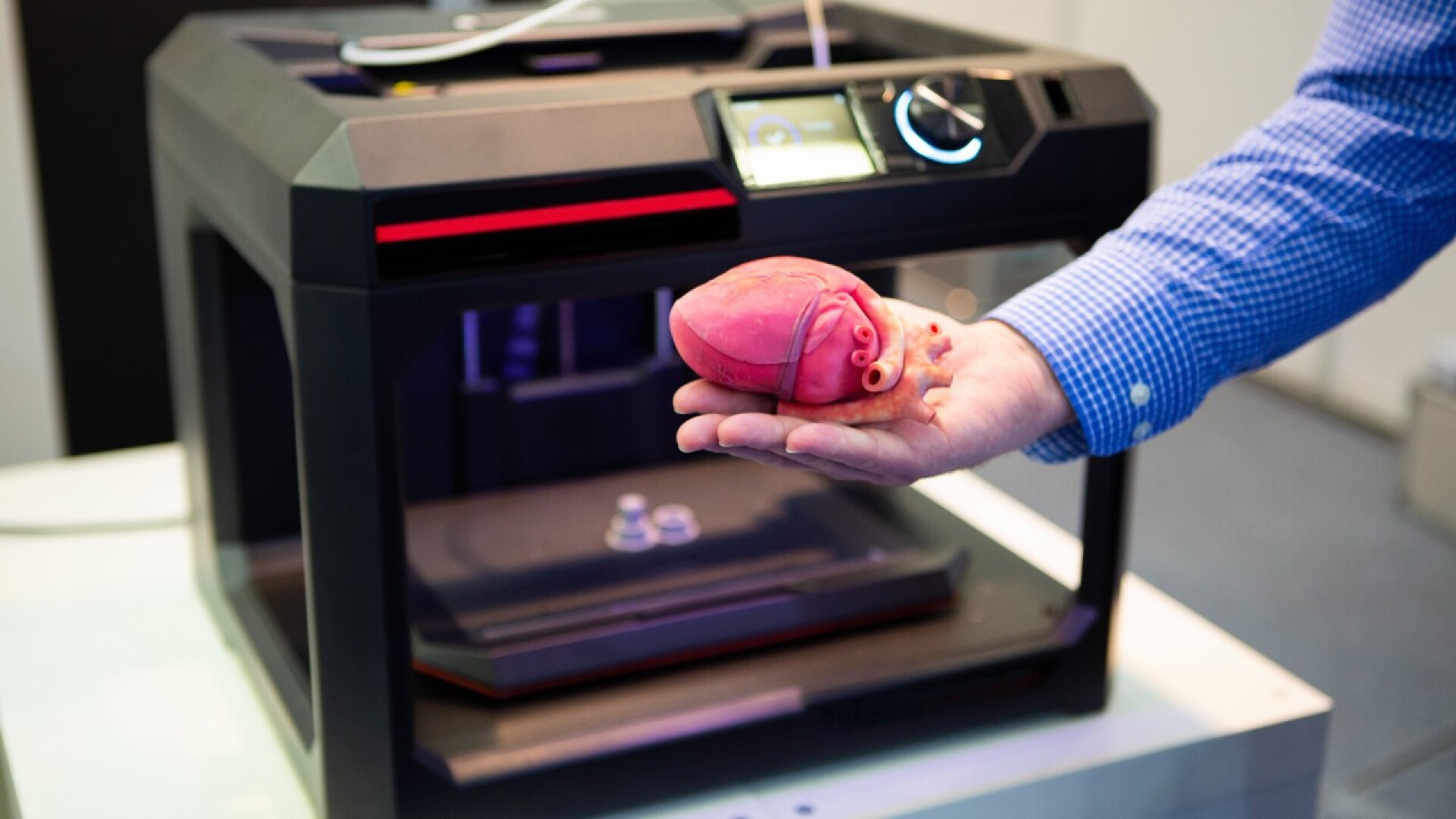
3D printing in medicine
3D printing is transforming medicine with advanced applications: from precise, patient-specific implants to research into biocompatible tissues, it offers completely new treatment perspectives.
3D printing has fundamentally transformed the medical landscape by offering innovative solutions for diagnostic, therapeutic and imaging applications. The foundations of this revolutionary process lie in additive manufacturing, which precisely builds up materials such as biocompatible polymers or even biological tissue, layer by layer. A central aspect of 3D printing in medicine is the production of anatomical models. These precise replicas of organs and tissues not only enable detailed visualization for doctors and surgeons, but also serve as crucial tools for pre-operative planning. Another key aspect is the individualized production of implants and prostheses. 3D printing enables these to be tailor-made and patient-specific, resulting in improved fit and functionality. Overall, the fundamentals of 3D printing in medicine lay the foundation for a new era of personalized medicine and help create more precise, efficient and patient-centered approaches to healthcare.
Applications of 3D printing in medicine: Revolutionary advances in patient care
3D printing has a wide range of applications in medicine. From the personalized production of implants to the manufacture of customized prostheses and bioprinting for tissue regeneration - the technology is revolutionizing medicine through innovative and individualized solutions. The experts at rapid.tech 3D can give you good advice in this area and introduce you to the latest developments.
3D printing in surgery
Additive manufacturing has enabled significant advancement in surgery, improving the accuracy of procedures and opening up new possibilities for precise planning and execution. One prominent application of 3D printing in surgery is the production of patient-specific surgical templates. The ability to produce anatomical models based on patient data using a 3D printer enables surgeons to plan complex procedures more precisely. The patient-specific models allow surgeons to familiarize themselves with individual anatomical structures and visualize different scenarios prior to an operation. This leads to improved accuracy and safety during the procedure. Another aspect of 3D printing in surgery is the production of customized implants, prostheses and orthoses. By customizing to a patient's anatomical needs, implants can be better integrated, leading to improved outcomes and faster recovery. 3D printing in surgery enables a more precise and individualized approach to complex medical cases. This innovative technology helps increase the effectiveness of surgical procedures while reducing recovery time for patients.

3D printing in pharmacy
It is also having a groundbreaking impact in the pharmaceutical industry. This innovative technology enables the production of customized medicines and is changing the way medicines are developed and dosed. By using 3D printers in pharmacy, pharmacies and pharmaceutical companies can produce personalized medicines for individual patient needs. A significant advantage of 3D printing in pharmacy is the ability to create customized dosages. This is particularly relevant when producing medicines for children or patients with specific needs. Precise dosing can help to minimize side effects and maximize the effectiveness of treatment. In addition, 3D printing in pharmacy enables the creation of medicines in different forms, such as easier-to-swallow tablets or fast-dissolving forms. This improves patient acceptance and compliance. In summary, 3D printing is transforming pharmacy by enabling personalized medicines and innovative dosage forms. This technology is helping to increase the effectiveness of drug therapy while improving patient care.
3D printing in dentistry
3D printing has initiated a groundbreaking transformation in dentistry. Precise 3D models of the tooth structure can be created, which serve as the basis for the individual production of implants, prostheses, crowns and bridges. These customized solutions not only improve the accuracy of fit, but also enable accelerated production and customization of dental products. By applying sophisticated 3D printing in dentistry, an exact reproduction of the natural tooth geometry is achieved, resulting in optimized functionality and aesthetics. Advanced 3D printing technology enables dentists to offer highly precise and patient-specific treatments, increasing both the efficiency and quality of dental care. 3D printing improves dentistry by expanding the possibilities of personalized dental care and contributing to an advanced, patient-centered practice.

Bioprinting: organs and tissue from the 3D printer
It has initiated a pioneering development in the field of bioprinting technology. It enables the precise creation of biological tissues and organs by building up cells and biomaterials layer by layer. Bioprinting opens up promising prospects for regenerative medicine and the replacement of damaged tissue. A key advantage of 3D printing in bioprinting is the ability to create complex structures that closely resemble natural tissue. Through the precise placement of cells and biomaterials, the functionality and biocompatibility of the printed tissue can be optimized. This enables the production of customized tissues for transplants or the development of tissue replacement models for pharmaceutical tests. Furthermore, 3D printing helps to accelerate the bioprinting process by enabling precise control over the three-dimensional arrangement of cells. The ongoing development of biomaterials and printing technologies opens up new horizons for the production of functional tissues and organs. 3D printing is transforming bioprinting technology by offering innovative approaches to the production of tissues and organs. This represents a significant step towards personalized medicine and regenerative therapies.

Advantages of 3D printing in medicine
Additive manufacturing has become a groundbreaking tool in medicine and offers a variety of advantages that are revolutionizing patient care and medical research. At Rapid.Tech 3D, you can exchange ideas with experts in the field of 3D printing in medicine and learn about the many advantages. We have already put together seven advantages of 3D printing in medicine for you here:
- Individual implants and prostheses: 3D printing in medicine can be used to create tailor-made implants and prostheses that correspond exactly to the patient's anatomical conditions. This enables a better fit and functionality, which leads to an improved quality of life.
- Surgical planning: Doctors can create anatomical models from 3D printing in medicine to better plan and visualize complex surgical procedures. This facilitates the precise positioning of implants and reduces the risk of complications during surgery.
- Manufacturing of Medical Instruments and Devices: 3D printing in medicine enables the manufacture of specially adapted medical instruments and devices, ranging from braces to surgical tools. These can be easily customized and optimized to meet the requirements of a specific procedure.
- Rapid Prototyping for Medical Devices: 3D printing in medicine enables rapid prototyping for medical devices. This speeds up the innovation process and allows prototypes to be created cost-effectively to test and refine new medical technologies.
- Easy Anatomy and Patient Education: The prints can create detailed models of anatomical structures that help doctors and patients better understand complex medical information. This contributes to improved education and decision-making.
- Cost-Efficiency: When producing medical devices in low volumes or customized solutions, 3D printing in medicine can be more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing methods. This is particularly beneficial for personalized medical devices.
- Faster research and development: 3D printing in medicine facilitates the research and development of new medical devices and therapeutic approaches. Prototypes can be quickly created and modified to test the effectiveness of new concepts before they are produced on a large scale.

Disadvantages of 3D printing in medicine
3D printing in medicine offers many advantages, but there are also some disadvantages and challenges that need to be considered:
- High cost: 3D printers and the materials used in the medical field can be very expensive to purchase. Specialized medical printers and biocompatible materials in particular increase costs.
- Lack of long-term studies: There are few long-term studies to date on the durability and effects of 3D printed implants or devices in the human body. Without sufficient data, risks could be overlooked.
- Training needs: Doctors and medical staff need to be trained to use 3D printing effectively, which means additional costs and time.
- Adaptation to specific patients: Although 3D printing enables personalized medicine, it can be difficult to find the perfect solution for each individual case because biological systems are very complex.
- Long development time: The design and manufacturing process for medical devices or implants can be time-consuming. It takes a lot of time to create precise models and test them before they can be used in practice.
- Regulatory hurdles: Medical products have to go through strict regulations and approval procedures. This also applies to 3D printed implants and devices, which can significantly delay the process.
- Material limitations: Not all materials available for 3D printing are biocompatible or suitable for use in the human body. This limits the choice of materials that can be used.

The future of 3D printing in medicine
The prospect of 3D printing in medicine promises groundbreaking developments that will revolutionize the way we understand healthcare. A crucial role is played by advancing technology, which enables highly complex structures and tissues to be printed with unprecedented precision. From customized implants to personalized medications, 3D printing in medicine opens up completely new perspectives for individual patient care. The increasing integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will further optimize the 3D printing process. By analyzing patient data, personalized models can be created that are precisely tailored to the needs of each individual. This not only enables more precise diagnoses, but also customized therapeutic approaches. The miniaturization of 3D printers in medicine opens up the possibility of integrating them directly into medical facilities. Doctors could thus print on site, which not only saves time, but also improves the availability of life-saving aids. The development of biocompatible materials even makes it possible to print complex tissues and organs, which could revolutionize transplants in the future.
Overall, the future of 3D printing in medicine is characterized by customized, efficient and highly precise patient care. This technology will not only push the boundaries of medical possibilities, but also usher in an era of personalized medicine.